Battery Introduction
In the battery sector, three main battery types are widely used and dominate the market: cylindrical, square and pouch. These cell types have unique characteristics and offer various advantages. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of each cell type and compare them based on various factors.
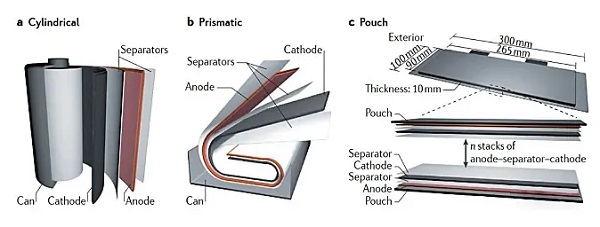
1. Cylindrical battery core
Advantage:
- Mature and cost-effective: cylindrical batteries have been in industrial production for more than 20 years, with mature manufacturing processes and high production efficiency. This means lower costs and higher product yields compared to other cell types.
- Excellent reliability and safety: cylindrical batteries offer excellent reliability and safety due to their extensively tested production methods and their steel casing for extra protection.
Disadvantages:
- Weight and size: The steel casing used in cylindrical batteries adds weight, resulting in lower energy density compared to other battery types. Furthermore, the cylindrical shape results in low space utilization.
- Limited capacity: The radial thermal conductivity of cylindrical batteries limits the number of winding layers, resulting in a smaller individual capacity. This results in EV applications requiring multiple batteries, which adds complexity and can lead to connection losses.
2. Square battery
Advantage:
- Enhanced protection: Square batteries are made of aluminum alloy or stainless steel casing, providing better protection compared to pouch batteries. This improves battery safety.
- Simplified structure and reduced weight: The square battery has a simple structure and uses lightweight materials. Compared with cylindrical batteries, it has higher energy density and lighter weight. This reduces the number of cells required for the battery module and reduces the requirements on the battery management system (BMS).
Disadvantages:
- Lack of standardization: The wide variety of square battery models on the market makes standardizing the process challenging. This can lead to reduced automation, significant differences between individual cells, and shorter battery pack life.
3. Pouch battery
Advantage:
- Enhanced safety: pouch batteries are packaged in aluminum-plastic composite film, which effectively reduces the likelihood of explosions compared to rigid casings used in alternative battery types.
- High energy density: pouch batteries are lighter, 40% lighter than steel-cased batteries of the same capacity, and 20% lighter than aluminum-cased batteries. This results in higher energy density.
Disadvantages:
- Standardization and cost challenges: pouch batteries face difficulties in achieving standardization, leading to rising costs. In addition, heavy reliance on imported aluminum-plastic films and low consistency pose challenges for pouch battery manufacturers.
Summarize
Each battery type (cylindrical, square, and pouch) has its own advantages and disadvantages. Cylindrical cells are cost-effective and offer excellent consistency, while prismatic cells offer enhanced protection and simplified construction. Pouch batteries offer high energy density but face challenges with standardization and cost. The choice of battery type depends on factors such as material properties, application requirements and product specifications. Regardless of cell type, safety is a critical issue and compliance with relevant safety standards is crucial.




